Crohn's disease can occur at any age, but is predominantly diagnosed in women and men aged 20-30 years, affecting on average 1 in 100 people worldwide.
Research shows that between 1.5% and 28% of people with Crohn's disease have a genetic predisposition to it.
What is Crohn's disease?
Crohn's disease is an inflammatory bowel disease that causes swelling of tissues in the digestive tract (usually the small and large intestines). Types of Crohn's disease include:
- ileitis. Swelling occurs in the ileum (lower part of the small intestine);
- ileocolitis. Inflammation develops in the ileum or colon;
- gastroduodenal (gastroduodenal) form. Irritation is localized in the stomach and upper part of the small intestine (duodenum);
- jejunoileitis. Foci of inflammation develop in the upper half of the small intestine (jejunum).
In some cases, the pathology affects only the large intestine. Crohn's disease is not contagious and is not transmitted from person to person. If you suspect intestinal inflammation, you should consult a gastroenterologist .
Causes of Crohn's disease
The exact cause of Crohn's disease is unknown, but scientists believe that a malfunction of the immune system plays a major role in the development of the pathology, causing immune cells to attack the digestive tract. Risk factors for Crohn's disease include:
- genetic predisposition;
- imbalance of intestinal microflora;
- smoking;
- bacterial infections (mycobacteriosis, E. coli);
- air pollution.
Those at risk of developing the disease include people who take antibiotics, birth control pills, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs without medical supervision. The likelihood of Crohn's disease increases with a high-fat diet .
What does Crohn's disease look like?
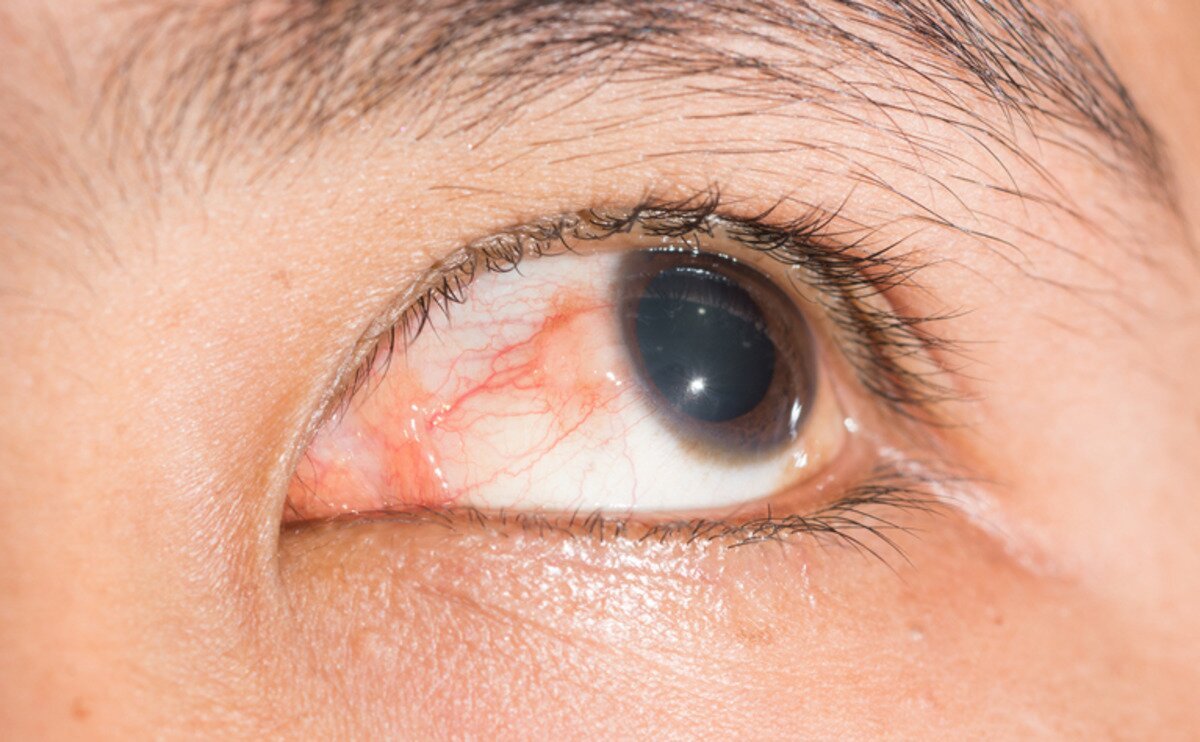
Crohn's disease in the mouth manifests itself as ulcerative lesions that cause discomfort and pain when swallowing. On the skin, the disease can cause rashes and erosions, which are localized in the abdomen and lower extremities. People with Crohn's disease can also have inflammation of the mucous membrane ( conjunctivitis ) and iris (iritis) of the eye. What Crohn's disease looks like can be seen in the photo.
- chronic diarrhea ;
- elevated temperature;
- constant fatigue;
- blood or mucus in the stool ;
- decreased appetite and weight loss;
- pain and burning in the anus ;
- discharge from the anus;
- a feeling of incomplete bowel movement (including after defecation);
- inflammation of the skin and joints;
- redness and irritation of the eyes.
Treatments for Crohn's Disease
It is impossible to cure Crohn's disease, since the pathology has an autoimmune nature, the course of therapy is aimed at reducing inflammation and relieving symptoms, preventing complications, achieving long-term remission. It is impossible to cure Crohn's disease with folk remedies, herbal tinctures, on the contrary, can increase the risk of consequences and progression of the pathology. Treatment of Crohn's disease may include:
- anti-inflammatory drugs (corticosteroids). Used to relieve inflammation in the intestines, usually used for a short period of time (approximately three to four months);
- immune system suppressors. Aimed at suppressing the body's immune response and blocking substances that cause inflammation;
- biopreparations. They are used to disrupt the “binding” of immune system cells and the intestinal mucosa;
- Antibacterial drugs. Antibiotics reduce the number of pathogenic bacteria and discharge from fistulas and abscesses (if they develop).
To relieve symptoms, the doctor may also prescribe antidiarrheal and painkillers. Vitamins are necessary for Crohn's disease if the body does not absorb enough nutrients. In case of pathology, vitamins B12, D, folic acid and iron supplements may be prescribed.
In severe cases of Crohn's disease, a patient may need surgery. The surgeon removes the damaged part of the digestive tract and then reconstructs healthy parts of the intestine.
Pregnancy is not contraindicated in Crohn's disease. During periods of exacerbation, fertility (ability to become pregnant) may decrease, but during remission it normalizes. During pregnancy, some medications used to treat the pathology may be harmful, so when planning a child , it is necessary to discuss with your doctor the adjustment of the course of therapy.



0 Comments